Table of contents
- What is Oracle?
- Importance of Oracle
- Oracle blockchain classification
- Top 5 outstanding Oracle blockchain projects
- The potential of the Oracle blockchain
1. What is Oracle?
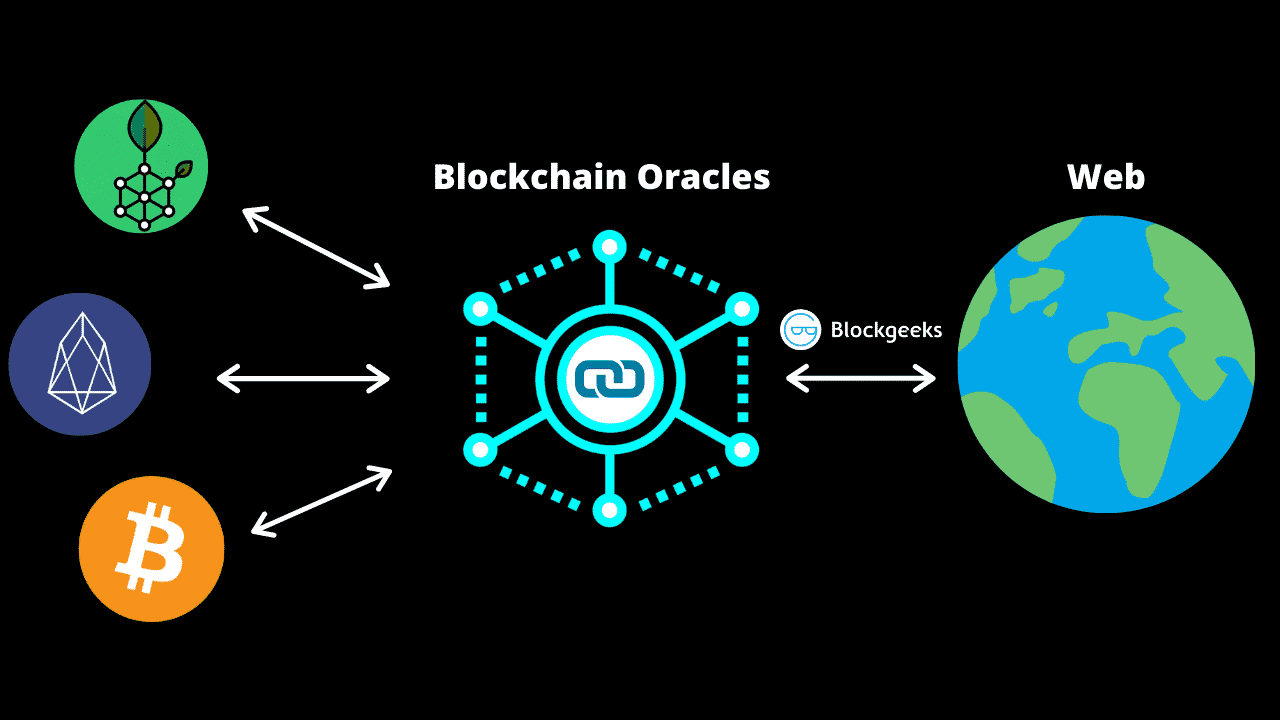
Oracle acts as a bridge between on-chain and off-chain (or between smart contracts and the outside world). Oracle provides real-world data for Web 3.0 ecosystems including: price data, online payments, temperature from sensors, results of sports tournaments,...
For example:
Price is one of the data that Oracle provides. With some lending platforms, they need to know the exact price of a token in order to value that token in borrowing/lending and liquidating assets. Oracle's task will now aggregate prices from many different exchanges. Then send it to that lending platform. This process will be carried out continuously to ensure the transparency and accuracy of the data.
2. Importance of Oracle
In the 21st century with the explosion of Big data and AI, Oracle is an indispensable part when it comes to acting as a data bridge for blockchains and retrieval to interact with the outside world. Blockchains using Oracle will be highly scalable and flexible. In addition, decentralized applications using Oracle will connect to most APIs to easily collect and verify data from various sources, for example:
- Price movement data of tokens/coins to ensure fairness and accuracy in loan/lending transactions, asset liquidation
- Exchange rates for OTC markets
- Mortgage rates and liquidity for decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
3. Oracle blockchain classification
Oracle hardware and software
Software Oracle
Software Oracle (Oracle software) will be responsible for processing some real-time data such as temperature, commodity prices, flight or train delay... then extracting the necessary information and transferring it to a smart contract. .
Hardware Oracle
Hardware Oracle is designed to collect information from physical devices such as barcode scanners, electronic sensors, etc. and feed it to smart contracts.
Oracle "send and receive"
Inbound Oracle
Inbound Oracle is a type of Oracle that is responsible for receiving data from external sources to smart contracts, often used in automated transactions.
Outbound Oracle
In contrast to Inbound Oracle, Outbound Oracles will send information from smart contracts to the outside.
Oracle Centralized and Decentralized
Centralized Oracle
Centralized Oracles are controlled by an organization and are the sole information provider for blockchains. Using only one source of information can be quite risky because the effectiveness of the smart contract will depend entirely on the organization that controls that Oracle. It is this centralization that will make Centralized Oracles more vulnerable to attack.
Decentralized Oracle
The Decentralized Oracle (Decentralized Oracle) will collect information from many external sources, increasing the reliability of the data provided. Smart contracts can query multiple oracles to determine the validity and accuracy of data, so Decentralized Oracles are said to be more reliable.
4. Top 5 outstanding Oracle blockchain projects
Chainlink
Chainlink is one of the pioneering projects in the Oracle field. Chainlink provides a real-world database for smart contracts through a decentralized Oracle. One of Chainlink's most popular services is price aggregation, which uses nodes to feed data off-chain to on-chain.
2021 is an extremely successful year for Chainlink with the number of Chainlink ecosystem projects surpassing 1000 and many other great strides. Hopefully in 2022, Chainlink will remain strong and maintain its "big brother" position in the Oracle blockchain segment.
Band Protocol
Band Protocol is an Oracle protocol that runs on top of the Cosmos blockchain. The project provides the ability to access and verify data outside of the dApp's blockchain. The long-term goal that the protocol is pursuing is to create an “Internet of blockchains”.
Band is famous for its Oracle solution for cross-chain. Band's input data are all reliable sources from many independent parties. BAND token holders will be involved in the governance of the protocol.
Nest Protocol
Nest Protocol is proud to be the first oracle network to produce and verify on-chain price data. At the same time, with its consensus mechanism, Nest can thrive on its data collection, pricing, and computation structure. Despite its recent establishment, Nest Protocol has made quite a strong impression with other projects in the same field.
DIA Protocol
DIA Protocol (DIA) is an open source blockchain, used to provide and verify data for dApps. DIA integrates its oracle infrastructure with Astar Network, a parachain running on Polkadot. Implementing oracle will make it easier for DeFi applications on Astar to connect to the data of the outside world.
API3
API3 is a protocol that connects dApps with different API libraries, allowing smart contracts to retrieve, exchange and verify data with the outside world. API3 can be compatible with dApp applications quite well, helping developers save a lot of time and cost in building applications.
In addition, API3 intends to allow API providers to operate their own nodes to save costs and shorten the cumbersome connection process that Oracle blockchains are experiencing.
5. The potential of the Oracle blockchain
Blockchain technology is currently being used quite a lot to develop a decentralized economy. However, smart contracts still have many limitations and have not really brought into full play their applications. The biggest downside of smart contracts is that they can't connect directly to real-world data.
The Oracle blockchain was born to thoroughly solve the above problem. The more applications that connect the real to the virtual, the stronger the Oracle blockchains will be.


.png)




